3D model Sheep skeleton VR / AR / lowpoly CGTrader

Skull Skeleton Sheep · Free image on Pixabay
Sheep Skeleton Sheep have 7 cervical vertebrae, 13 thoracic vertebrae, 6 lumbar vertebrae, 4 fused sacral vertebrae and between 3-24 caudal vertebrae. The skull is dome-shaped and slants downwards. Each side of the lower jaw of the sheep is held together by a ligament which allows lateral movement of the jaw when they are chewing.

Sheep Skeleton Stock Illustration Getty Images
Our Sheep Anatomy chart shows more information on this topic: https://www.anatomystuff.co.uk/sheep-anatomy-chart-poster-laminated.htmlDiscover more with our.
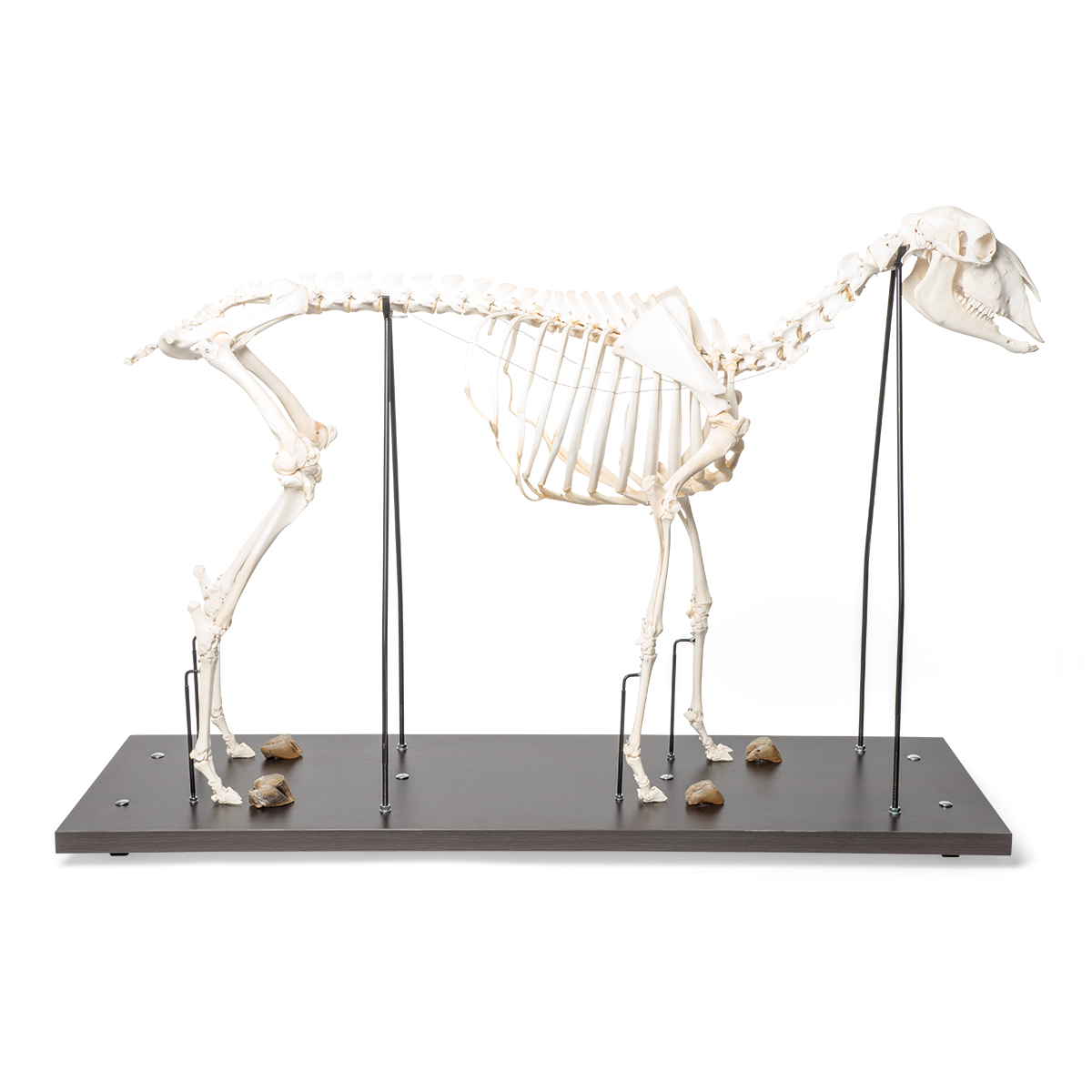

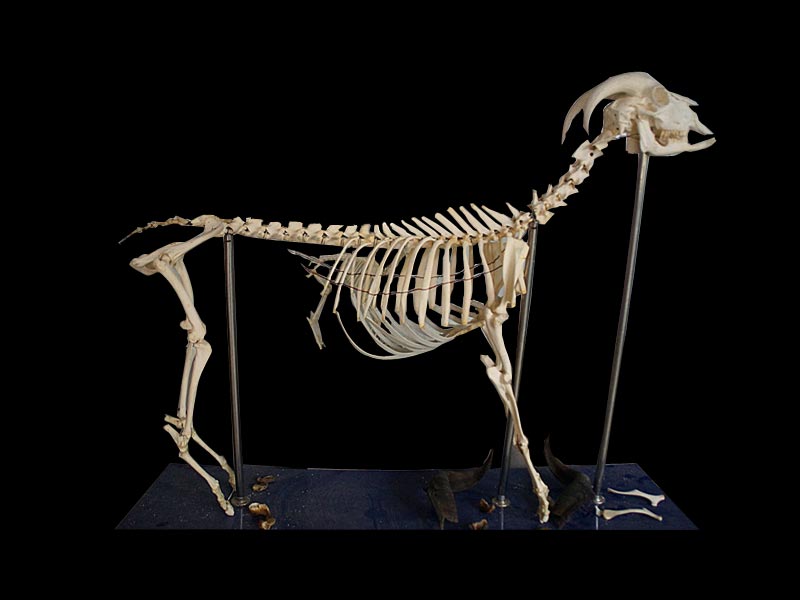
Domestic Sheep Skeleton (Ovis aries), Male, Specimen 1021025
The sheep skeleton consists of five types of bones: long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones. Long bones, such as the femur and humerus, are the most extended bones in the body and provide support and leverage for movement.

X Veterinary study of a sheep skeleton Sheep, Sheep anatomy
Anatomy of the sheep spine and its comparison to the human spine. 1997 Apr;247 (4):542-55. doi: 10.1002/ (SICI)1097-0185 (199704)247:4<542::AID-AR13>3..CO;2-P. The sheep spine is often used as a model for the human spine, although the degree to which these spines are anatomically comparable has yet to be categorically established. The purpose.

Sheep Anatomy Skeleton Sheep Anatomy Google Search Sheep Pinterest
The rest of the skeleton of all these animals (except the fish) also has the same basic design with a skull that houses and protects the brain and sense organs and ribs that protect the heart and lungs and, in mammals, make breathing possible. Each of the four limbs is made to the same basic pattern.

Sheep Skeleton Free Stock Images & Photos 4823452
SHEEP CONFORMATION WHAT IS CONFORMATION? Conformation is the anatomy and skeletal function and how it impacts the animal's health, adaptability, longevity, and productivity. Made up of Structure, Balance, and Soundness, plus breed traits. Visual confirmation scores run from 1-5. 1=best 5=worst SOUNDNESS
_skeleton.jpg)
Ram's Horn Ram Anatomy
sheep, (Ovis aries), species of domesticated ruminant (cud-chewing) mammal, raised for its meat, milk, and wool.The sheep is usually stockier than its relative the goat (genus Capra); its horns, when present, are more divergent; it has scent glands in its face and hind feet; and the males lack the beards of goats.Sheep usually have short tails. In all wild species of sheep, the outer coat.

Sheep Skeleton by larvitice on DeviantArt
This genuine sheep skeleton is the perfect way for veterinary students to study the anatomy of Ovis aries.This sheep skeleton model is complete and can be used for both mammalian and comparative anatomy studies. Consisting of approximately 215 individual bones, which are rigidly connected to each other, this sheep skeleton represents a typical example of the order of even-toed ungulates.

sheep skeleton Google Search Sheep Pinterest Skeletons
The skeleton of sheep is subject to the same inherited, metabolic, toxic and inflammatory disease processes as most other animal species. However, published reports of specific diseases of the ovine skeleton are uncommon.
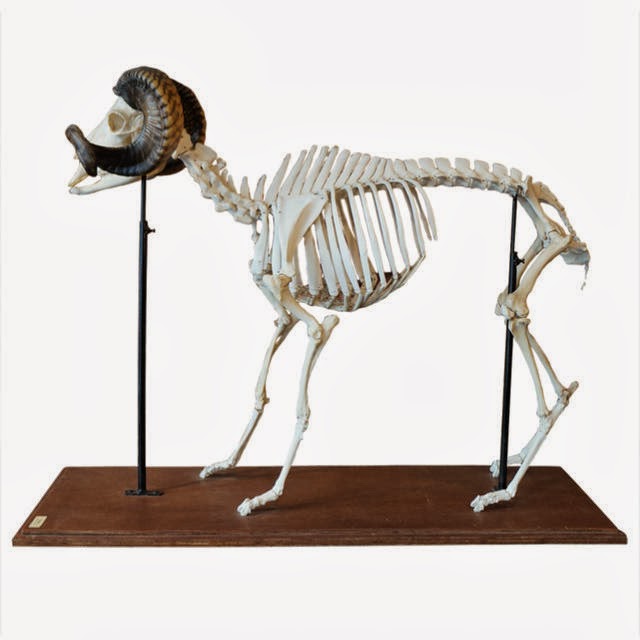

Ram's Horn Ram Anatomy
Sheep ( pl.: sheep) or domestic sheep ( Ovis aries) are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term sheep can apply to other species in the genus Ovis, in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates.
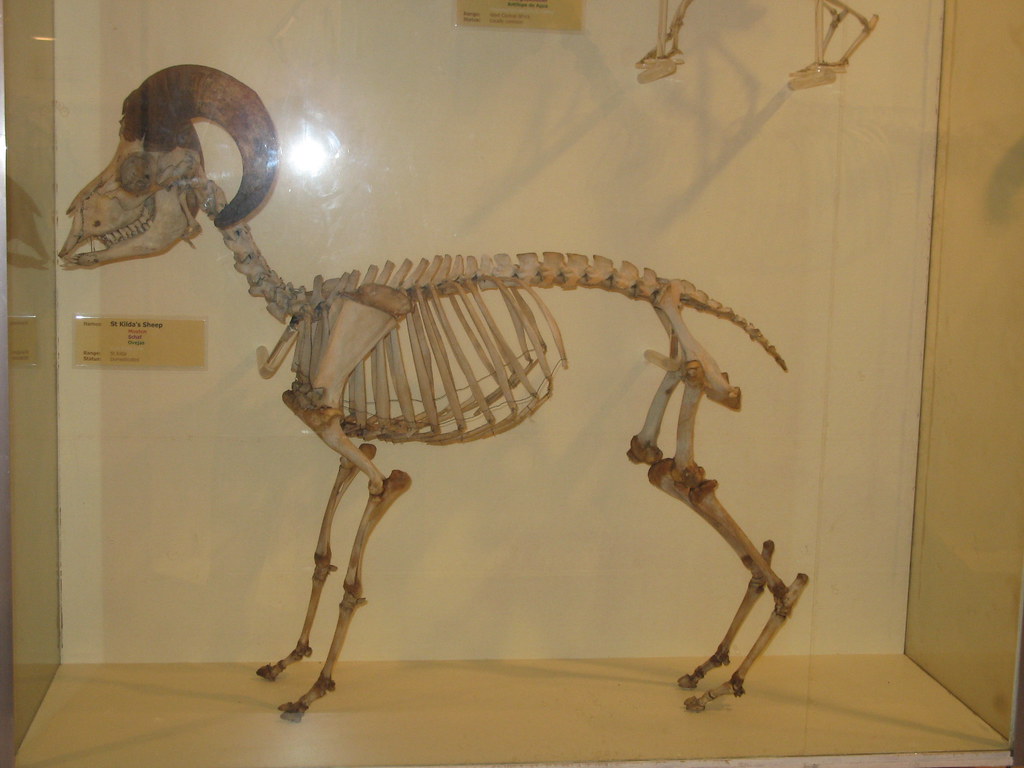

Sheep Skeleton Alicestronaut Flickr
A sheep's skull is composed of the maxilla, the frontal bone, the sphenoid bone, the occipital bone, and the parietal bone. The maxilla is located above the eye sockets. It is used as leverage for the ophthalmic muscles to attach to the skull. The frontal bone is located on the top and front of the head.

Sheep bone specimens,animal skeleton specimens,medical teaching model
Sheep are fascinating creatures with unique anatomical features. Understanding the structure of a sheep's skeleton is crucial for farmers, veterinarians, and animal enthusiasts alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different bones, joints, and functions of a sheep's skeletal system. Why is Understanding Sheep Anatomy Important?
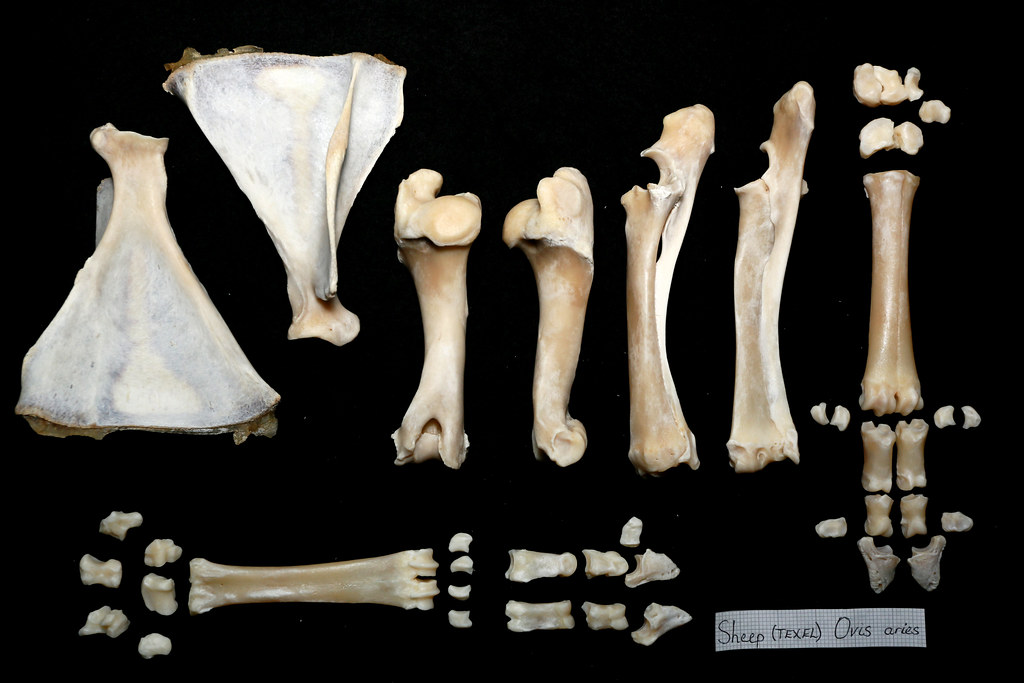
Sheep skeleton Fore limbs John Rochester Flickr
Atlas, Anatomy of sheep is prepared to be simple and sufficient for the needs of the veterinary students . The diagrams and illustrations, which profess considerable accuracy of detail, are drawn from carefully dissected specimens and treated by computer programs for application of nomenclature of the different structures .
Bighorn Sheep Skeleton Photos, Diagrams & Topos SummitPost
The skeleton of the loin, sirloin and rump Sheep pelvis In a live animal, the vertebrae act like a suspension bridge to support the weight of the abdomen.

Sheep Skeleton With Polymelia Photograph by Patrick Landmann/science
Background Information: The sheep brain is remarkably similar to the human brain. One major difference, however, is in proportion. For example, the sheep brain has a proportionately smaller cerebrum. Another difference is in orientation of the spinal cord. The sheep spinal cord is orientated anterior to posterior, as in any four-legged animal.
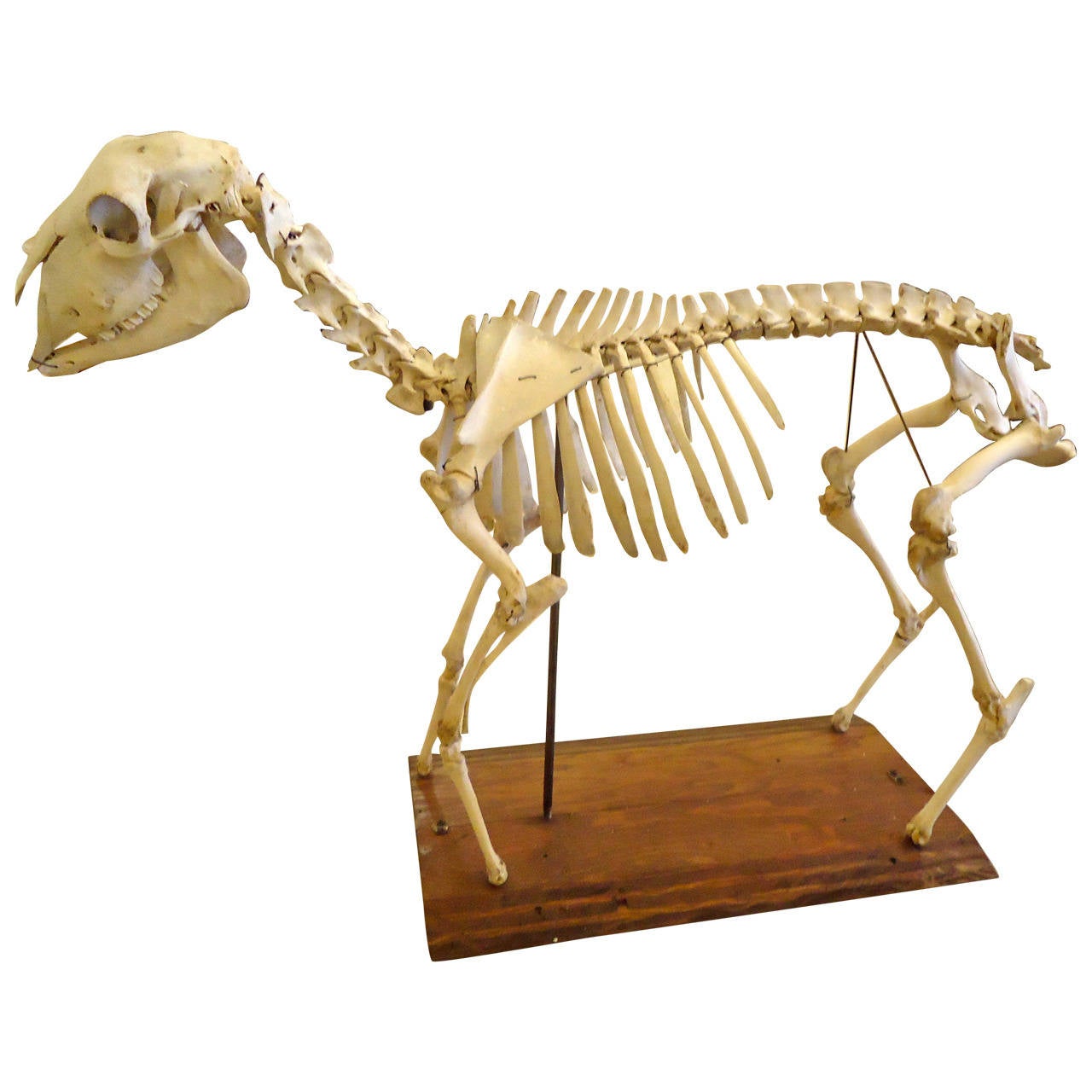

Striking Skeleton of a Sheep at 1stdibs
Body Structure Sheep have a unique body structure that allows them to graze on grass and other plants. Their necks are long and flexible, allowing them to bend down to eat. Their legs are short but sturdy, and their hooves are divided into two toes, which provide excellent traction on uneven terrain. Behavior and Welfare